Chemical Structure:
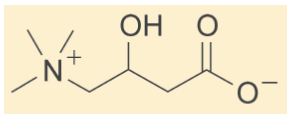
L-Carnitine is a trimethylated amino acid. Carnitine is a nutrient that helps the body turn fat into energy. It is produced by the body in the liver and kidneys and stored in the skeletal muscles, heart, brain and sperm. L-Carnitine is a co-factor required for transformation of free long-chain fatty acids into acylcarnitines, and for their subsequent transport into the mitochondrial matrix, where they undergo betaoxidation for cellular energy production. Carnitine is made in the body from breaking down muscle protein and converting it to carnitine. Methionine and lysine serve as pre-cursors to the synthesis of L-Carnitine. High stress levels, parenteral nutrition patients and elderly individuals may not be able to synthesize sufficient quantities of L-Carnitine. Under these circumstances L-Carnitine is considered a conditionally essential nutrient and supplementation may be required.
Benefits of L-Carnitine in liver:
• L-Carnitine deficiency causes liver disease.
• L-Carnitine decreases brain and blood ammonia levels by stimulating urea genesis.
• L-Carnitine effectively protects mitochondrial function; hence administration of L-Carnitine could prevent hepatitis.
Other Benefits of L-Carnitine:
• L-Carnitine improves lipid profiles in individuals with hyperlipidemia with reductions in total and LDL-cholesterol and increased plasma apo-lipoprotein A-1 and B levels.
 Clinical Evidences
Clinical Evidences
• L-Carnitine administration reverses acute mental status changes in a chronic hemodialysis patient with hepatitis C infection.
We suspect that subclinical liver dysfunction and dialysis status in tandem contributed to the carnitine deficiency, hyperammonemia, and confusion and that the L-carnitine administration reversed these biochemical and clinical abnormalities.
Clin Nephrol. 2002 May;57(5):402-5.
• Role of carnitine as a therapeutic agent in chronic liver disease. Therefore carnitine plays important role in liver disease.
Life Sci. 1996;59(19):1579-99
• L-carnitine treatment reduces steatosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with alpha-interferon and ribavirin.
The results of this study suggests that L-carnitine may have a role among the reduction of steatosis strategies in patients with hepatitis C treated with IFN alpha and ribavirin.
Dig Dis Sci. 2008 Apr;53(4):1114-21.Epb 2007 Oct 16